In the digital age, the concept of self-sovereignty is transforming how we manage our personal data. At the Hannover Messe, our demo project for the “MERLOT Self Sovereignty Manager” (SeSoMan), showcased how this innovative approach empowers individuals to be the Sovran over their own Data. The User Journey presented is illustrated in this article.
What is the Self Sovereignty Manager?
Data self-sovereignty empowers individuals to have ownership and control over their personal data across services, enhancing privacy and personalization. The MERLOT Marketplace’s Smart Education Services utilize personal data to provide tailored recommendations and improve AI services, while respecting data sovereignty to provide a controlled user-centered approach to share own data with services.
The MERLOT project emphasizes the importance of self-sovereignty, where individuals remain the owners and managers of their data. The Self-Sovereignty Management System (SeSoMan) framework supports data control, consent management, and transparency, allowing users to track and manage their data sharing and consent, while promoting trust and security. Although SeSoMan’s full implementation is beyond the scope of the MERLOT project, the DEMO was designed to address the key principles of what a user-centered self-sovereign exchange of data between two (Advanced) Smart Education Services could look like .
The Use-Case: Fatma’s Journey
To understand the practical benefits of SeSoMan, let’s follow Fatma, a student navigating the complexities of data sharing between her school’s administrative system “Sokrates” from bit media and a career recommendation service “Karriereassistent” from Schülerkarriere.
Step 1: Logging into Sokrates
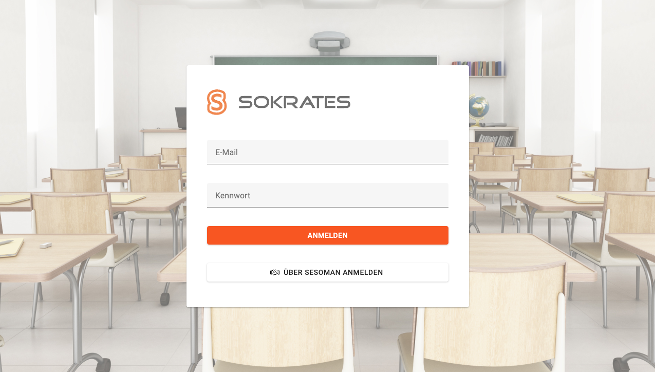
Fatma starts her journey by logging into her school’s administrative system, Sokrates. Using SeSoMan, she authenticates her identity securely. SeSoMan acts as a gateway, providing a notification that asks for permission to log into the System. This step ensures that Fatma’s consent is explicitly given before any interaction with her data starts to happen.
Step 2: Connecting Services
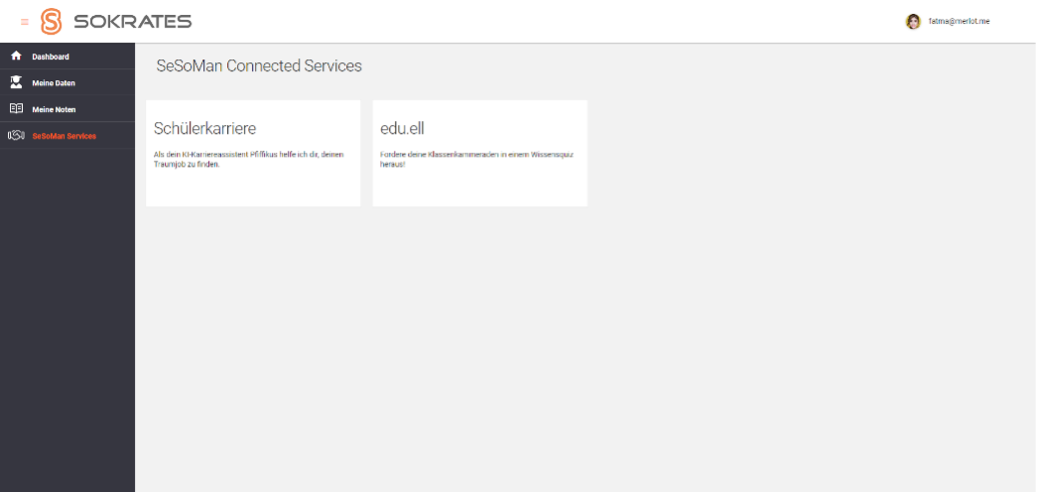
Once logged into Sokrates, Fatma encounters a list of “Connected Services” that can access her data. She sees that the Karriereassistent, is listed as one of these services. Fatma is intrigued by the potential of receiving personalized career recommendations by it and decides to explore the Karriereassistent further.
Step 3: Exploring the Karriereassistent
Fatma reviews the Karriereassistent without logging in, gaining insights into how the platform could benefit her. The platform’s interface presents an overview of its capabilities, highlighting the personalized recommendations it offers. Karriereassistent then prompts Fatma to log in to access her data from Sokrates.

Step 4: Logging into the Karriereassistent via SeSoMan
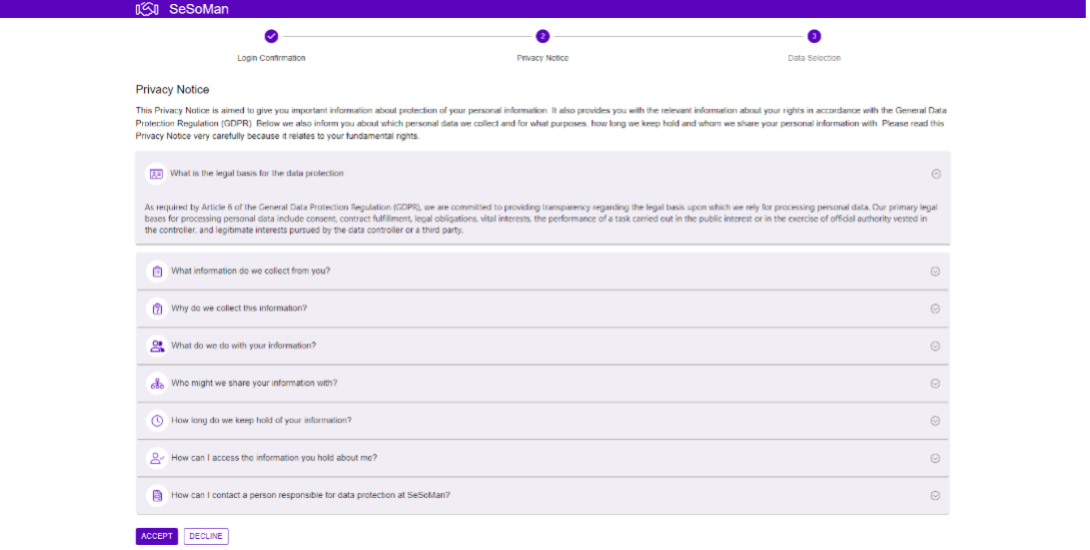
Fatma uses SeSoMan again to log into Karriereassistent. The SeSoMan sends a notification requesting permission to access the platform and displays a privacy notice detailing how Fatma’s data will be used. This transparency is crucial for informed consent, ensuring that Fatma understands how her data will be processed.

Step 5: Reviewing Privacy Notices and giving consent
Before data transfer occurs, the SeSoMan presents Fatma with the service Privacy Notice explaining how her data will be used and processed.
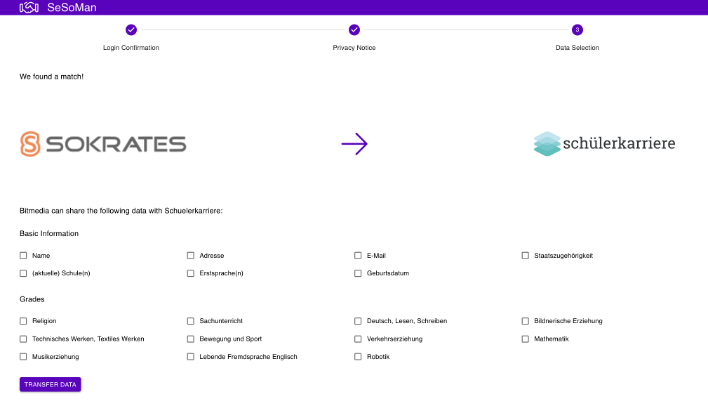
Once Fatma consents to the Privacy Notice, a structured view of the data available for sharing from Sokrates to Karriereassistent is presented. Fatma can select which specific data she wishes to share. This ensures that only the data Fatma deems necessary is transferred, maintaining her ownership, control and data privacy.
Step 6: Data Transfer and Confirmation
After selecting the data, Fatma confirms the transfer. The Karriereassistent then notifies her that the data transfer was successful. Fatma is redirected to the Karriereassistent, where she finds her data available under e.g. the “Lebenslauf” section. Additionally, SeSoMan provides a link to its dashboard, allowing Fatma to review the privacy notice and consented receipt associated with the data transfer. Here she can easily see what access was given to what service and also deny further access to here data for some or all the services.

The Self Sovereignty Manager concept presented at the Hannover Messe is demonstrating a future where individuals have full control over their personal data. By following Fatma’s journey, we see how SeSoMan enhances privacy, facilitates secure data transfers, and builds trust between users and digital services. As the digital world continues to advance, SeSoMan will be a key player in ensuring that user sovereignty remains at the core of data interactions.

